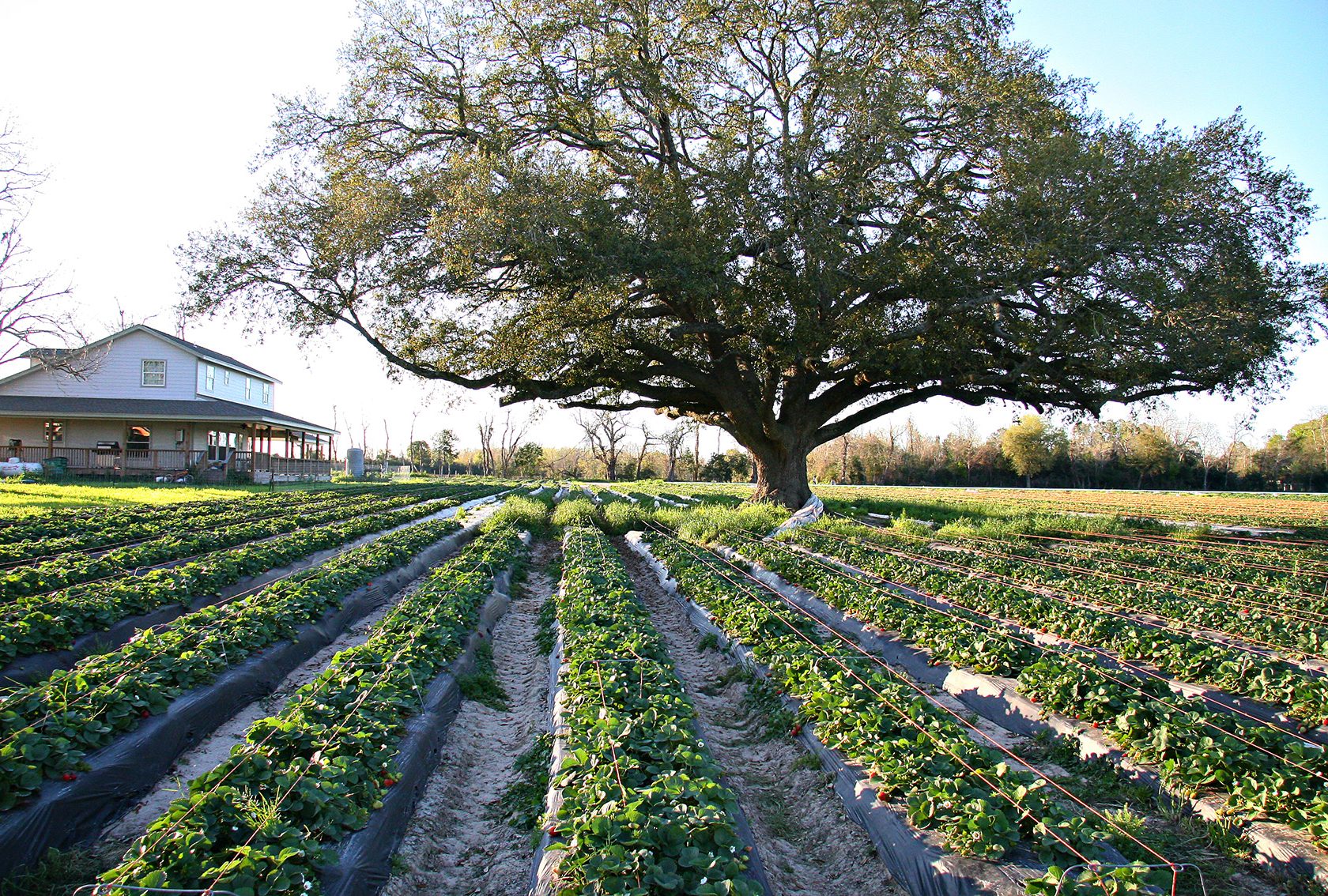
Strawberry patch is more than just a place where strawberries grow; it's a haven for nature lovers, gardening enthusiasts, and foodies alike. Whether you're planning to start your own strawberry patch or simply curious about how these juicy berries are cultivated, this article will guide you through everything you need to know. From planting and maintenance to harvesting and enjoying the fruits of your labor, this comprehensive guide ensures you're well-equipped with expert advice and actionable tips.
Growing strawberries in a patch is a rewarding experience, offering not only fresh, delicious produce but also a sense of accomplishment. With the right techniques and care, anyone can create a thriving strawberry patch in their backyard or even in containers. This guide dives deep into the essential steps and considerations, ensuring that your strawberry patch becomes a source of pride and joy.
In this article, we will explore the intricacies of creating and maintaining a strawberry patch, from selecting the right location to troubleshooting common issues. We'll also provide valuable insights into the nutritional benefits of strawberries, their varieties, and how to maximize your harvest. By the end of this guide, you'll have a thorough understanding of how to grow and enjoy strawberries like a pro.
Read also:Andrew Deluca Actor The Rising Star In Television Drama
Table of Contents
Introduction to Strawberry Patch
A strawberry patch is a dedicated area where strawberry plants are cultivated to produce fresh, flavorful berries. These patches can range from small backyard gardens to large commercial farms. Regardless of the scale, the principles of growing strawberries remain the same: proper planning, care, and maintenance are essential for a successful harvest.
Strawberries are perennial plants, meaning they can produce fruit for multiple seasons if cared for properly. They thrive in temperate climates and require specific conditions to grow optimally. A well-maintained strawberry patch not only provides a steady supply of fresh berries but also adds beauty to your garden with its lush green foliage and vibrant red fruits.
Before diving into the specifics of creating a strawberry patch, it's important to understand the basics. This includes knowing the different types of strawberries, their growth requirements, and the benefits of growing them. By the end of this section, you'll have a solid foundation to build upon as you embark on your strawberry-growing journey.
Benefits of Growing Strawberries
There are numerous advantages to growing your own strawberry patch. Beyond the joy of harvesting fresh, organic berries, cultivating strawberries offers several health, economic, and environmental benefits.
Nutritional Benefits
Strawberries are packed with essential nutrients, making them a powerhouse for health-conscious individuals. Here are some key nutritional benefits:
- Rich in vitamin C, which boosts immunity and promotes skin health.
- Contain antioxidants like flavonoids, which help reduce inflammation and fight free radicals.
- Low in calories but high in fiber, aiding digestion and promoting weight management.
Economic Savings
Growing your own strawberries can save you money in the long run. Instead of purchasing expensive organic strawberries from the store, you can enjoy fresh, homegrown berries at a fraction of the cost. Additionally, homegrown strawberries often taste better and are free from harmful pesticides.
Read also:Innovative Icevf Advancements And Impact On Modern Technology
Environmental Impact
By growing strawberries in your own patch, you contribute to a more sustainable lifestyle. Home gardening reduces the carbon footprint associated with transporting store-bought produce. Moreover, you can control the use of fertilizers and pesticides, ensuring your strawberries are grown in an eco-friendly manner.
Choosing the Right Location
The success of your strawberry patch largely depends on selecting the right location. Strawberries thrive in specific conditions, and choosing an appropriate site is crucial for their growth and productivity.
Sunlight Requirements
Strawberries require at least 6-8 hours of direct sunlight daily. When selecting a location, ensure it receives ample sunlight throughout the day. Avoid areas with excessive shade, as this can hinder fruit production and lead to weak plants.
Soil Conditions
Strawberries prefer well-drained, loamy soil with a pH level between 5.5 and 6.8. Conduct a soil test before planting to determine its pH and nutrient content. If the soil is too acidic or alkaline, amend it with organic matter or lime to achieve the ideal balance.
Accessibility and Space
Choose a location that is easily accessible for maintenance and harvesting. Ensure there is enough space for the plants to spread and grow. If space is limited, consider using raised beds or containers to maximize your growing area.
Preparing the Soil
Proper soil preparation is a critical step in creating a thriving strawberry patch. Healthy soil provides the foundation for robust plant growth and bountiful harvests.
Clearing the Area
Begin by clearing the chosen area of weeds, rocks, and debris. Weeds compete with strawberry plants for nutrients and water, so it's essential to remove them thoroughly. Use a hoe or hand-pull weeds to ensure the area is clean and ready for planting.
Improving Soil Quality
Incorporate organic matter such as compost or well-rotted manure into the soil to improve its fertility and structure. This not only enhances nutrient availability but also improves drainage and aeration. Spread a 2-3 inch layer of organic matter over the soil and work it in using a garden fork or tiller.
Mulching
Mulching is an effective way to retain soil moisture, regulate temperature, and suppress weed growth. Use straw, pine needles, or wood chips as mulch, applying a 2-3 inch layer around the plants. Avoid piling mulch directly against the stems to prevent rot and pest issues.
Planting Strawberries
Planting strawberries correctly is essential for establishing a healthy strawberry patch. Follow these steps to ensure your plants get off to a strong start.
Choosing the Right Time
The best time to plant strawberries depends on your climate. In temperate regions, early spring is ideal, while in warmer climates, fall planting may be more suitable. Check local gardening guidelines to determine the optimal planting time for your area.
Planting Techniques
When planting strawberries, ensure the crown (the point where the roots meet the stems) is level with the soil surface. Planting too deep or too shallow can lead to poor growth or rot. Space the plants 12-18 inches apart in rows, with 2-3 feet between rows to allow for air circulation and easy maintenance.
Watering
Water the plants thoroughly after planting to help them settle into the soil. Strawberries require consistent moisture, especially during flowering and fruiting. Aim to provide 1-2 inches of water per week, either through rainfall or irrigation.
Strawberry Varieties
There are several strawberry varieties to choose from, each with unique characteristics and growth habits. Selecting the right variety for your patch can significantly impact your harvest.
June-Bearing Strawberries
June-bearing strawberries produce a single, large crop in late spring or early summer. They are ideal for those who prefer a concentrated harvest and are great for making jams, preserves, and desserts.
Ever-bearing Strawberries
Ever-bearing strawberries produce two smaller crops, one in spring and another in late summer or early fall. They are perfect for gardeners who want a steady supply of berries throughout the growing season.
Day-Neutral Strawberries
Day-neutral strawberries produce fruit continuously throughout the growing season, regardless of day length. They are a great choice for small gardens or container planting, offering flexibility and consistent yields.
Maintenance and Care
Once your strawberry patch is established, ongoing maintenance is key to ensuring healthy plants and abundant harvests. Regular care and attention will help your strawberries thrive.
Fertilization
Strawberries benefit from regular fertilization to support their growth and fruit production. Use a balanced fertilizer with equal parts nitrogen, phosphorus, and potassium (NPK) every 4-6 weeks during the growing season. Avoid over-fertilizing, as this can lead to excessive foliage growth at the expense of fruit production.
Pest and Disease Management
Monitor your strawberry patch regularly for signs of pests and diseases. Common pests include aphids, slugs, and spider mites, while diseases like powdery mildew and gray mold can affect plant health. Use organic pest control methods and remove infected plants promptly to prevent the spread of disease.
Pruning
Prune your strawberry plants to remove old leaves, runners, and weak stems. This improves air circulation, reduces the risk of disease, and directs energy toward fruit production. For June-bearing varieties, cut back foliage after harvesting to encourage new growth.
Harvesting and Storing
Harvesting strawberries at the right time and storing them properly ensures you enjoy their peak flavor and freshness. Here's how to make the most of your strawberry patch harvest.
When to Harvest
Strawberries are ready to harvest when they are fully red and slightly soft to the touch. Pick them in the morning when the berries are cool, as this helps preserve their flavor and quality. Use scissors or pinch the stems to avoid damaging the fruit.
Storing Strawberries
Store harvested strawberries in a cool, dry place. Avoid washing them until just before use, as excess moisture can cause them to spoil quickly. Place them in a single layer in a shallow container and cover with a damp cloth to maintain freshness.
Preserving Strawberries
If you have a surplus of strawberries, consider preserving them for later use. Options include freezing, making jams, or drying them. Each method has its own advantages, allowing you to enjoy strawberries year-round.
Common Issues and Solutions
Growing strawberries can present challenges, but with the right knowledge, you can overcome them and maintain a healthy strawberry patch.
Yellowing Leaves
Yellowing leaves are often a sign of nutrient deficiency or overwatering. Check your soil's nutrient levels and adjust fertilization accordingly. Ensure proper drainage to prevent waterlogged roots.
Fruit Rot
Fruit rot can occur due to excessive moisture or poor air circulation. Mulch around the plants to keep fruit off the soil and improve airflow. Avoid overhead watering to minimize moisture on the berries.
Bird Damage
Birds are attracted to ripe strawberries and can cause significant damage. Use netting or row covers to protect your patch from birds and other wildlife.
Conclusion
Creating and maintaining a strawberry patch is a fulfilling endeavor that offers numerous benefits, from fresh, nutritious berries to a sustainable and eco-friendly lifestyle. By following the steps outlined in this guide, you can establish a thriving strawberry patch that yields delicious fruits for years to come.
Remember to choose the right location, prepare the soil meticulously, and provide ongoing care to ensure your plants thrive. Whether you're a seasoned gardener or a beginner, growing strawberries is a rewarding experience that connects you with nature and provides a sense of accomplishment.
We hope this guide has inspired you to start your own strawberry patch. Share your experiences, tips, and questions in the comments below, and don't forget to explore other gardening resources on our site for more expert advice. Happy gardening!