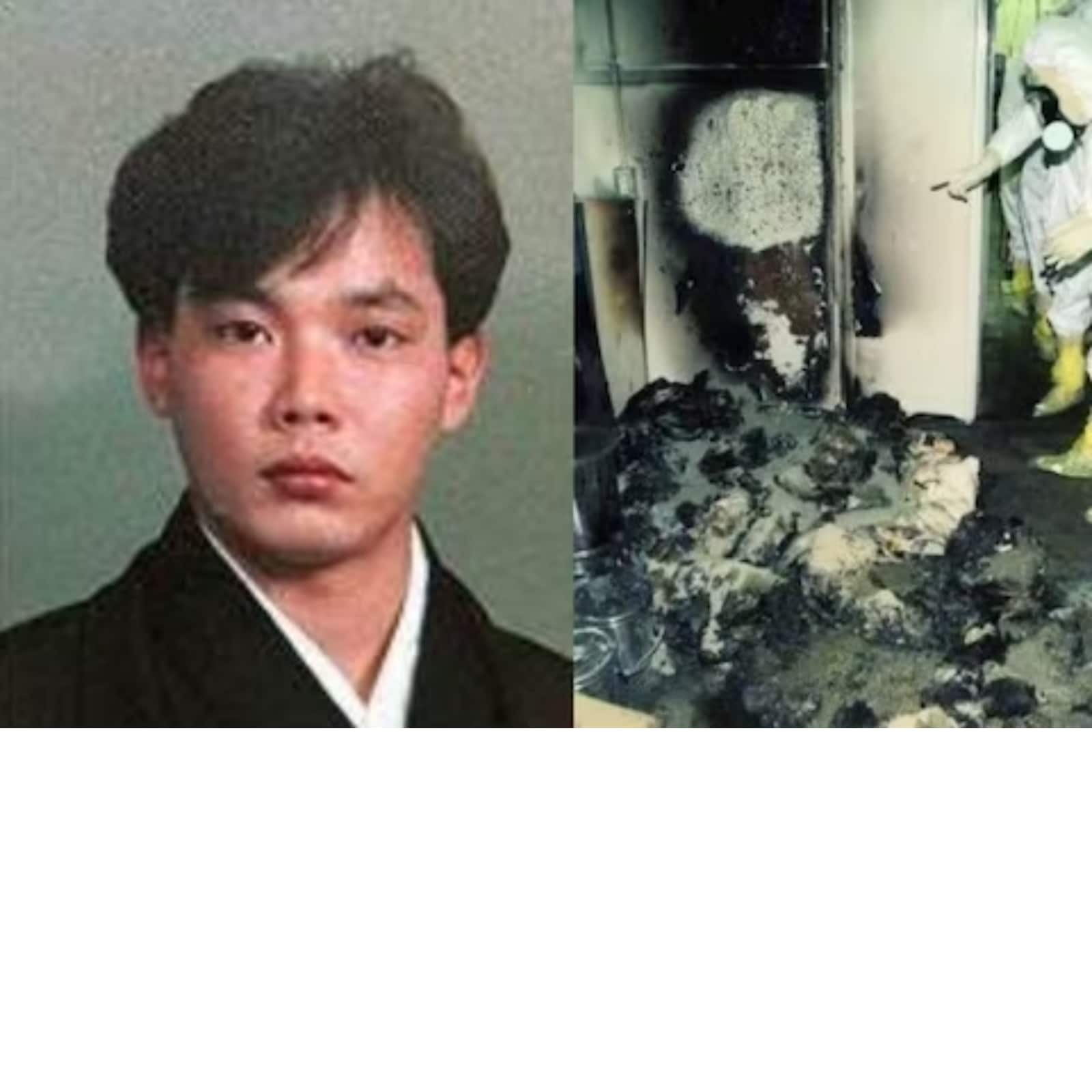
Hisashi Ouchi POS refers to the tragic incident involving Hisashi Ouchi, a Japanese nuclear worker who suffered severe radiation exposure during a criticality accident at a uranium processing facility in 1999. This event not only highlighted the dangers of working in nuclear environments but also served as a pivotal moment for the implementation of stricter safety protocols in the industry. Hisashi Ouchi’s story is one of resilience, suffering, and a grim reminder of the potential consequences of human error and inadequate safety measures. The term "POS" in this context refers to "Point of Safety," a concept that underscores the importance of stringent safety standards in hazardous workplaces. Ouchi's case remains one of the most severe radiation exposure incidents in history, prompting global discussions on the need for enhanced safety systems in nuclear facilities.
The incident involving Hisashi Ouchi occurred at the JCO nuclear fuel processing plant in Tokaimura, Japan. During the accident, a criticality event led to an uncontrolled nuclear chain reaction, releasing lethal doses of radiation. Ouchi, along with two other workers, was exposed to extreme levels of radiation. While his colleagues survived with severe injuries, Ouchi’s exposure was so extreme that it led to his prolonged suffering and eventual death. This catastrophic event prompted a reevaluation of safety protocols in nuclear facilities worldwide, emphasizing the importance of the "Point of Safety" concept to prevent such tragedies in the future. Hisashi Ouchi POS became a rallying cry for improved safety measures in hazardous industries.
Hisashi Ouchi’s case continues to resonate in discussions about workplace safety and nuclear energy regulation. The tragedy exposed systemic failures in safety protocols, worker training, and emergency response systems. It also highlighted the critical need for a "Point of Safety" mindset in industries dealing with hazardous materials. By examining the lessons learned from this incident, we can better understand the importance of implementing robust safety measures and fostering a culture of accountability and preparedness. This article delves into the life of Hisashi Ouchi, the details of the accident, and the broader implications of his story for workplace safety and nuclear energy regulation.
Read also:What Does Frsc Stand For A Comprehensive Guide To Its Meaning And Importance
Table of Contents
- Biography of Hisashi Ouchi
- What Happened During the Criticality Accident?
- Why Are Safety Protocols Important in Nuclear Facilities?
- What Lessons Were Learned from the Hisashi Ouchi Incident?
- How Did the Incident Impact Global Nuclear Safety Standards?
- Understanding Hisashi Ouchi POS: A Framework for Safety
- How Can Worker Training Prevent Future Accidents?
- What Does the Future Hold for Nuclear Safety Measures?
Biography of Hisashi Ouchi
Hisashi Ouchi was born on March 1, 1962, in Japan. He grew up in a modest household and pursued a career in the nuclear industry, motivated by the promise of stable employment and the opportunity to contribute to Japan’s energy needs. Ouchi began working at the JCO nuclear fuel processing plant in Tokaimura, where he was employed as a technician. His role involved handling uranium and ensuring the safe processing of nuclear materials. Despite his dedication to his work, the lack of adequate safety measures and training would ultimately lead to his tragic fate.
Personal Details and Bio Data
| Full Name | Hisashi Ouchi |
|---|---|
| Date of Birth | March 1, 1962 |
| Place of Birth | Japan |
| Occupation | Nuclear Technician |
| Employer | JCO Nuclear Fuel Processing Plant |
| Date of Incident | September 30, 1999 |
| Date of Death | December 21, 1999 |
What Happened During the Criticality Accident?
The criticality accident at the JCO nuclear fuel processing plant occurred on September 30, 1999, when workers, including Hisashi Ouchi, were manually mixing uranium oxide with nitric acid in a precipitation tank. This process was part of the uranium enrichment procedure, but it violated safety protocols. The workers bypassed standard procedures, leading to an uncontrolled nuclear chain reaction. The reaction released a blue flash of radiation, exposing the workers to lethal doses. Hisashi Ouchi received the highest level of radiation exposure, estimated at 17 sieverts, far exceeding the lethal dose of 5 sieverts.
Immediate Aftermath
Following the accident, emergency services were called to the scene. Hisashi Ouchi and his colleagues were rushed to the hospital, where they underwent extensive medical treatment. Ouchi’s condition was critical, with severe damage to his internal organs, skin, and DNA. Despite the best efforts of medical professionals, his body could not recover from the extreme radiation exposure. The incident highlighted the inadequacies in emergency response systems and the lack of preparedness for such catastrophic events.
Systemic Failures
- Lack of proper safety training for workers
- Failure to adhere to standard operating procedures
- Inadequate emergency response protocols
Why Are Safety Protocols Important in Nuclear Facilities?
Safety protocols in nuclear facilities are essential to prevent accidents and protect workers and the surrounding environment. These protocols include guidelines for handling radioactive materials, emergency response plans, and regular safety audits. The Hisashi Ouchi incident underscores the dire consequences of neglecting these protocols. In Ouchi’s case, the workers were not adequately trained, and the procedures they followed were not aligned with safety standards, leading to the criticality accident.
Components of Effective Safety Protocols
Effective safety protocols in nuclear facilities should include the following components:
- Comprehensive training programs for all employees
- Strict adherence to standard operating procedures
- Regular safety drills and emergency response exercises
- Use of advanced monitoring and detection systems
Importance of a "Point of Safety" Mindset
The concept of Hisashi Ouchi POS emphasizes the need for a proactive approach to safety. By prioritizing safety at every stage of operations, nuclear facilities can minimize risks and prevent accidents. This mindset involves fostering a culture of accountability, where every worker is responsible for maintaining safety standards and reporting potential hazards.
Read also:Sky Mill Crafting Recipe Master The Art Of Sky Mill Creations
What Lessons Were Learned from the Hisashi Ouchi Incident?
The Hisashi Ouchi incident served as a wake-up call for the nuclear industry, prompting significant changes in safety regulations and practices. One of the key lessons learned was the importance of adhering to safety protocols and ensuring that workers are adequately trained. The accident also highlighted the need for improved emergency response systems and better communication between workers and management.
Global Reforms in Nuclear Safety
In the aftermath of the incident, Japan and other countries implemented stricter safety regulations for nuclear facilities. These reforms included:
- Mandatory safety training for all nuclear workers
- Enhanced monitoring and reporting systems
- Regular audits and inspections of nuclear facilities
Role of Technology in Preventing Accidents
Advancements in technology have played a crucial role in improving nuclear safety. Automated systems and real-time monitoring tools help detect potential hazards and prevent accidents. The Hisashi Ouchi POS framework emphasizes the integration of technology into safety protocols to create a safer working environment.
How Did the Incident Impact Global Nuclear Safety Standards?
The Hisashi Ouchi incident had a profound impact on global nuclear safety standards. It prompted international organizations, such as the International Atomic Energy Agency (IAEA), to review and update their safety guidelines. Countries around the world adopted stricter regulations to ensure the safety of nuclear workers and the public.
Key Changes in Safety Standards
Some of the key changes in global nuclear safety standards include:
- Implementation of stricter safety protocols
- Increased emphasis on worker training and education
- Development of comprehensive emergency response plans
IAEA’s Role in Promoting Safety
The IAEA played a pivotal role in promoting nuclear safety by providing guidelines and conducting safety assessments. Their efforts have helped create a safer and more accountable nuclear industry.
Understanding Hisashi Ouchi POS: A Framework for Safety
Hisashi Ouchi POS represents a framework for prioritizing safety in hazardous industries. This concept emphasizes the importance of creating a culture of safety, where every worker is responsible for maintaining high safety standards. By adopting this framework, organizations can prevent accidents and protect their employees.
Key Principles of Hisashi Ouchi POS
The key principles of Hisashi Ouchi POS include:
- Proactive risk management
- Accountability at all levels
- Continuous improvement of safety protocols
Benefits of Implementing Hisashi Ouchi POS
Implementing the Hisashi Ouchi POS framework can lead to numerous benefits, including:
- Reduced risk of accidents
- Improved worker morale and productivity
- Enhanced reputation and trust
How Can Worker Training Prevent Future Accidents?
Worker training is a critical component of preventing future accidents in hazardous industries. By providing comprehensive training programs, organizations can ensure that workers are equipped with the knowledge and skills needed to perform their jobs safely.
Elements of Effective Worker Training
Effective worker training programs should include:
- Hands-on training sessions
- Simulated emergency scenarios
- Regular refresher courses
Role of Leadership in Training
Leadership plays a crucial role in promoting a culture of safety. By prioritizing worker training and investing in safety education, leaders can create a safer and more accountable workplace.
What Does the Future Hold for Nuclear Safety Measures?
The future of nuclear safety measures is likely to be shaped by advancements in technology and increased global cooperation. As the nuclear industry continues to evolve, organizations must remain vigilant in their efforts to prioritize safety and prevent accidents.
Emerging Technologies in Nuclear Safety
Emerging technologies, such as artificial intelligence and machine learning, are expected to play a significant role in improving nuclear safety. These technologies can help detect potential hazards and prevent accidents before they occur.
Global Collaboration for Safety
Global collaboration is essential for advancing nuclear safety. By sharing best practices and working together, countries can create a safer and more sustainable nuclear industry.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
What is the significance of Hisashi Ouchi POS?
Hisashi Ouchi POS emphasizes the importance of prioritizing safety in hazardous industries. It serves as a reminder of the need for stringent safety protocols and a proactive approach to risk management.
How did the Hisashi Ouchi incident impact nuclear safety regulations?
The Hisashi Ouchi incident led to significant reforms in nuclear safety regulations, including stricter safety protocols, enhanced worker training, and improved emergency response systems.
What lessons can be learned from the Hisashi Ouchi tragedy?
The Hisashi Ouchi tragedy highlights the importance of adhering to safety protocols, providing adequate worker training, and fostering a culture of accountability and preparedness.
For more information on nuclear safety, you can visit the International Atomic Energy Agency (IAEA) website.
Conclusion
The story of Hisashi Ouchi POS serves as a poignant reminder of the importance of safety in hazardous industries. By learning from past mistakes and implementing robust safety measures, we can create a safer and more accountable workplace. The legacy of Hisashi Ouchi continues to inspire improvements in nuclear safety, ensuring that such tragedies are not repeated.